What Is a Full Port Ball Valve
Share:
Industrial valves serve several important functions, and to be able to handle that level of work, they come in varying sizes and shapes. Larger valves are meant for bigger pipes and related machines, and the material used in their construction has to match their sizes if they are to work as intended.
Our focus today is on full port ball valves. We are going to look into what they are, how they function, how they differ from other valves around. If you have been curious to know what full port valves are all about, then stick around to the end and learn a thing or two that will come in handy for you.
What is Full Port Ball Valves

Source: Pinterest
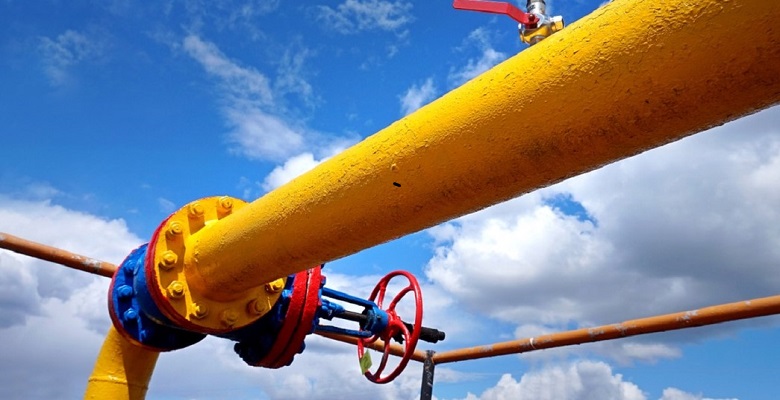
A full port ball valve is a unique type of valve that permits unrestricted flow once the valve is opened. They tend to have larger bodies compared to standard valves, and this has the capacity to use a larger ball with a bigger opening on the inside.
In most cases, the forged ball valves have the same size of openings as the pipes they serve, and this makes them a great component to have when setting up systems that have little to no flow loss. Once the full port valve is set to on in the open position, then it feels like there’s no valve in the way at all, allowing any material to pass through smoothly.
The Full Port Valve Design

Source: Pinterest
The design of a full port steel ball valve is not the same as most of the other types. It begins with a straight flow path, thanks to the larger opening, which allows unrestricted flow through the given medium. The site of the pipe that is being regulated by the full port valve usually has the same diameter as the valve.
This is to ensure that nothing leaks once the valve is closed shut. Operating this valve is not complicated at all since the ball inside the valve comes with a tiny hole that is smaller than the tube it is connected to. The purpose of this is to cause a pressure drop after the flow is restricted. This setup acts as a safety mechanism that ensures pressure doesn’t get out of hand as that could damage both the tubing and the valve.
Determining if you Need a Full Port Valve

Source: Pinterest
Full port valves are not used for every application, even when they fit. They are much bigger and may not be appropriate for small-scale operations. So how do you tell whether you need a full port ball valve over a standard one?
There are some applications that require a full port and nothing less, and you can tell this by studying the flow resistance. If the suction pump of a pipe, for instance, experiences pressure drops, this can impact the performance of the entire structure, and you will need to go with full port valves to counter this so that the flow can be maintained at a constant rate.
The default option for pumps and tubes is the standard ball valve unless otherwise, and the main reason for this is the fact that it is a cost-effective way of controlling the flow in a variety of applications. Standard ports also come in handy where there are space limitations that can impact the overall design of the entire system. Situations like this would require a much smaller ball valve, and the best option would be a full port valve.
Materials used to Make Full Port Ball Valves

Source: Pinterest
Like regular ball valves, full port ball valves are constructed using varying types of materials depending on their intended use. The following are some of the common materials that you will likely come across in the market today.
PVC: Polyvinyl Chloride is a common material used in making valves due to its ability to stay for long, its flexibility, and the fact that it doesn’t suffer from rust. Full port valves made using PVC tend to be cheaper and come in a wide range of colors.
Bronze: Bronze combined with brass is the ideal metallic material to make full port valves that are intended for systems that use lower pressure. The materials are resistant to corrosion and can hold their ground for a very long time before replacements are needed.
Stainless Steel: This is a more robust material that has the advantage of being rust-resistant and being strong enough to handle high pressures without collapsing. Full port valves made using stainless steel are a little heavier and cost more than PVC and Bronze, but they can handle geothermal systems that rely on high temperatures.
CPVC: This is Chlorinated PVC that is similar to regular PVC, with the only difference being that CPVC can handle higher temperatures. Full port ball valves constructed using CPVC can be used comfortably in systems that require high temperatures.
Iron: It may not be as flexible as PVC but when it comes to making ball valves that can withstand high temperatures and pressures then iron would be your best bet. The only drawbacks are that iron is heavy and is prone to corrosion.
Advantages of Full Port Ball Valves

Source: Pinterest
There are benefits that you accrue from using full port ball valves when compared to using regular ones. Some of these benefits include the following.
They provide the unrestricted flow of materials through a tube or a pipe system to the maximum level. Full port industrial ball valves have the widest openings among all valves, and this makes them the ideal option to go for when dealing with high pressures.
They provide an airtight seal when closed minimizing losses and leaks in the process. When dealing with gases and liquids, you have to be extra careful with the valves that you chose to go with. If they are not reliable, that can translate to huge losses, something that valve suppliers are very wary of.
Owing to their sizes, they are easy to open and close. All it takes is a swift movement of the wheels, and the floodgates are either opened full or sealed completely shut. An operation that can be handled by one person.
They are versatile enough to be designed for both big and small-scale operations. This is the reason why you are most likely to find full port valves in a geothermal plant. When made with the right material, they can be used for just about anything.
Maintenance and repair are an easy affair, and there’s no need to dismantle the entire system to get this done. Full port ball valves are made up of detachable parts which can be cleaned independently, and this increases efficiency.
They are of high-quality design, and this gives them longevity and the ability to handle high pressure and temperature systems without collapsing. This is the reason full port ball valves are used in heavy industries around the world.
The Standard Port Ball Valve Design

Ball valves are used in the manufacturing industry for their extensive fluid and pressure control operations. Their vacuum interiors make them great contenders in oil and gas applications. Moreover, they require lower torque than other valves like globe valves, butterfly valves, gate valves, and many others. Depending on the ball valve manufacturers, they are available in various materials and component designs. They are durable and flexible, making them easier to use and control among multiple manufacturing operations. They are typically used for piping activities and are classified based on their size as standard port valves and full bore valves.
The main difference between a standard port valve and a full-bore one is the size of the fluid flow opening. A standard port valve comes with an entrance that is smaller and more compact than the fuller one. Because of this, the pressure buildup and drop are higher. The smaller hole design makes the flow much more constricted, rapidly increasing the valve’s pressure. This can pose several risks during application. Standard ball valve openings are smaller than the pipe diameter, while a full bore ball valve has a fluid space equal to the pipe diameter.
However, they have an economical design compared to full port or full bore ball valves, adding to their simplicity and affordability. They are smaller and narrower and are helpful when the manufacturing line demands high pressure. Since they are also available in ratings that accommodate lower pressure, standard ball valves prove to be much more versatile.
A standard port valve is a ball valve with a smaller fluid flow hole. They are classified based on their opening size. A standard port valve is designed to carry out the following functions in piping industries:
- Coolants
- Mixers
- Pneumatic circuits
- Fluid flow
- Liquid fillers
- Processors
The design of a standard port is relatively straightforward. Their inlet connections are of the exact measurement as the pipe. However, the ball present in the main component has a smaller opening, creating pressure from the restricted fluid flow. It has a straight path for movement, and the outlet connections are the same as the pipe diameter.
Full Port Ball Valve Vs. Standard Port
Different valves are named after the primary component for fluid flow control. For instance, the porous ball component controls the fluid movements in a ball valve. It comprises a hole that lets the liquids and gasses in. With a quarter-turn design, every 90-degree turn would close or open the hole for the shut-in and shut-off applications. Ball valves are classified based on their relative sizes of components, especially the fluid opening in the ball in the main element.
The essential difference is that the pipe diameter for a full port valve is the same as the fluid opening in the ball. However, the holes are narrower than the pipeline diameter regarding standard port sizes. Generally, they are available in width, one size more limited than a pipe. They are as follows:
Full Port (Bore) Ball Valve

Definition
Full port ball valves consist of a direct path flow for the fluids. This ensures that the pressure drop is kept to a minimum, and there is no movement resistance when it comes to flowing gasses and liquids. When fully open, they create less pressure than a straight ball valve, preventing high-pressure drop emergencies and risks in usage. It also contains the rate of fluid flowing from dropping to extreme amounts.
There are also fewer chances of bubble formation due to rapid pressure decreases. When repeated, such bubble formations are dangerous for the piping system and can depreciate the pipelines. A full bore valve reduces cavitation and maintains the flowing rate of various fluids.
Bore Size
The opening size is the main difference that sets apart a full port valve from a standard one. The opening to fluid movement is compared to the pipeline diameter and overall size in classifying the two. As in the name, a full bore ball valve has a full-width hole size and is directly comparable to the pipe size. For instance, a full valve will have a bore size of 3/4th of an inch if the diameter is also 3/4th. The rule of thumb is that full port ball valves always equal the pipeline diameter and come in configurations that match the size of the pipeline.
Flow Coefficient
Flow coefficients are defined as the degree of resistance of the primary fluid movement component. In this case, the part is the ball. The coefficient is similar to the pipeline, enabling minor to no resistance for fluid movements.
Standard Port Ball Valves
Definition
As mentioned, their hole sizes are one size shorter than the diameter, causing a full-blown pressure drop. A standard port valve comes with an opening that is smaller and more compact than the fuller one. Because of this, the pressure buildup and decline are higher. The hole size is not subjective, as they are compared to the diameter of the pipe. Standard ball valve openings are smaller than the pipe diameter, while a full bore ball valve has a fluid space equal to the pipe diameter. The smaller hole design makes the flow much more constricted, rapidly increasing the valve’s pressure. This can pose several risks during application.
Bore Size
A standard ball valve is typically found in smaller sizes than the diameter of pipelines, but the degree varies per configuration and among manufacturers. They are typically found one size shorter than the standard pipeline diameter (or full bore ball valves). Using a full port ball valve, standard ball valves will be found in bore sizes of ½ an inch for a ¾-inch pipeline.
Flow Coefficient
The high pressure and resistance created in the ball region account for the high number in terms of flow coefficient.
When To Use Standard Port Ball Valves
Port valves are customarily classified and categorized into several types based on many factors. The two most common factors are based on size and construction. There are a plethora of different ball valves in the industrial market, which makes it challenging to choose. Therefore, knowing the applications of a standard ball valve can prove essential in getting the right kind based on industrial requirements.
A standard ball valve creates a straight path for fluid movements and flowing control. They are characterized by having high pressure when wholly open and creating restricted flow. Although the main body is the same size as the pipeline connected to it, since it is located inside the main component, the bore size is kept a tad bit smaller than the diameter of the channel.
Due to the above reasons, they are generally equipped for those industrial applications that demand a compact design and high-pressure outlets. They are an affordable option for high-pressure applications by taking up less space. Standard port ball valves are equipped when high turbulence and pressure are required. However, the manufacturing plant must adequately accommodate pressure hikes and disturbed flowing. They are mostly used to carry out the following industrial applications:
- Rapid shut-out and shut-in functions
- Fast switch on and switch off
- Straightforward processes
- Uncomplicated manufacturing operations
- High durability
- Tight sealing to prevent leakage and damage
Although the flow rate is exposed to ups and downs in every piping system, it is essential to know the factors which affect it to prevent drastic changes. The flow rate is negligible when choosing between standard port valves and full-bore ones. The three most common factors are as follows:
- Length of the pipelines
- Number of sections in the pipe
- Bends and faults in the pipe
- Other external conditions
When To Use Full Port Ball Valves

Knowing the applications and uses of a full port or full bore ball valve can prove essential in choosing the right kind for the relevant industrial setting and requirement. A full port ball valve has a straight path for a fluid passage like a standard ball valve. However, it offers almost no resistance in the movement, making the liquids and gasses pass through without much force or pressure. It promotes smoother flow and is usually applicable in those industries where pressure sensitivity is a crucial factor. The fluids have a more comprehensive range for flowing.
The diameter of the pipe is used as a base for manufacturing this ball valve, essentially making them equal for zero resistance. They have a bi-directional movement of fluids and are usually available with a quarter-turn or half-turn design. A quarter-turn design enables the full port valve to stop or allow liquids to penetrate and pass through it every 90-degree turn.
The applications of a standard port valve can also be executed by a full port one, but with added features. While a standard one cannot reduce pressure, full port ones offer a variety of pressure ratings, including lower ones. They are on the higher side of the financial spectrum. They are usually used when the flow rate must be kept constant. Along with the applications of a standard ball valve, a full bore ball valve can be used for the following requirements:
- Solid, semi-solid, liquids, and gas media are involved in flowing
- Pipes for pumping and suctions
- Smooth flow
- Prevention of material buildup
- Prevention of separations in material
As flow restrictions cause buildups and diversion in material flow, full port valves are recommended where various media flow through the pipes. They are equipped with an open and exposed design, preventing materials from accumulating around the connection. This can be a high-risk scenario for standard port valves and contribute to poor performance in the long run. They are also widely used in suction pipes, as pressure hikes can damage the operation of the pump.
Conclusion
Full port ball valves are very reliable tools in high-pressure tubing and piping systems. They are not hard to operate and are of simple design, yet they handle a very important role in the manufacturing process. If you are looking to set up a plant that makes use of ball valves but have no idea where to begin your search, then check out our website at any time of the day, and all the questions you may have will be answered by our very able team of experts.