What is a Gas Valve?
The most common types of valves used to maintain the flow of oil and gas in industrial pipelines are gas valves. These devices ensure crude oil, refined gas, natural gas, and other materials reach their destination. So basically, a gas valve is employed in the pipelines to regulate the flow of oil and gas. A gas valve features an aperture that helps control the opening and closing amounts of liquids and gases allowed through pipes. It regulates the media flow by stopping and starting, adjusting the quantities, monitoring the direction, and regulating and relieving the pressure.
Since the environment inside the pipeline may vary according to their application, different types of valves have been developed over the years. While some are suitable for highly corrosive media, others are ideal for high-pressure applications. Due to these variants, each valve has its own pros and cons. One must understand their uses within the oil and gas industry for successful operation and application. Its most common types include the butterfly, slam-shut, check, gate, globe, ball, and plug valves. All of them are used in industrial, commercial, and residential applications for modulating and control purposes.
Gas valves are ideal for aerospace, agriculture, automotive, semiconductor, construction, food processing, medical, petroleum, maritime, cryogenic, mining, and many more. The most common materials used for constructing a gas valve include stainless steel, ductile iron, copper, aluminum, brass, sintered bronze, and steel.
Some gas valves are also constructed using a variety of plastics, including acetal, Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPC), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF). When installing a new gas valve, it is recommended to use a bubble test to ensure no leakages. The test is performed using a mixture of soap and water applied to all the gas line connections. Any leakage will cause bubbles to form in the soapy water, following which the fitting needs to be redone.
Typically made up of brass, a gas valve is designed not to create a spark when turned. Because it is available in several different types and materials with various functionalities, selecting the ideal one is challenging. That’s why it is helpful to consider the primary function for which it must be used. Consider whether the environment involves much pressure or if there is a need for any additional safety measures offered by slam-shut valves.
Valves are an essential part of any piping system in the oil and gas industry. Valves help regulate the flow of materials to and from machinery and equipment. This makes them integral in the many different kinds of functions and applications. Valves in the oil and gas industry have to work with liquids, gasses, viscous materials, and corrosive mediums.
At any given time, a single factory may have a number of different kinds of valves installed, each performing a different function. Valves in oil and gas factories can be used to start and stop the flow. Some valves can also be used to regulate the flow according to the pressure and velocity requirements. This article features a list of common valves used in the oil and gas industry, along with their function, pros, and cons.
Table of Contents
What Types of Valves are Used in the Oil and Gas Industry?
There are a number of different processes that take place inside and oil and gas factory. Each of those processes requires different kinds of materials to be taken to and from machinery and equipment. This means a number of different kinds of valves are needed for a single process to be successfully completed. Here is a list of some of the most common valves used in the oil and gas industry.
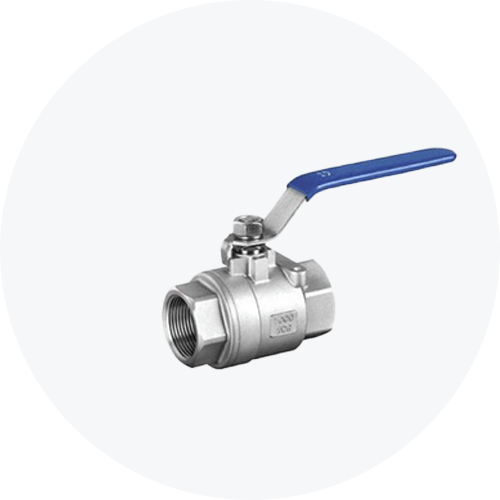
#1. Ball Valves
Ball valves are quarter-turn valves that provide quick shut-off and turn-on operation. These valves feature a sphere or a ball with a hollow center. When the center aligns with the pipe, the valve is open and allows the flow of the medium. When the ball turns, the center is no longer aligned with the pipe and the flow stops.
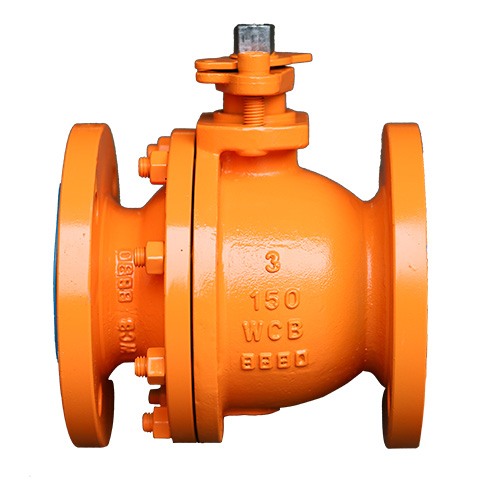

The stem and ball of these valves are usually made of some kind of metal while the seat is made of soft materials like Teflon. This combination of materials helps the ball valves work in temperatures as low as -200 degrees Centigrade and as high as 500 degrees Centigrade. Ball valves are very versatile and can be used to regulate the flow of liquids, gasses, and air. They are very famous in the industry because they provide a tight seal and a low torque. The only con of using ball valves is that they can only be used for shut-off applications, they cannot be used for throttling.
Common Ball Valves Used in Oil and Gas Industry
- Trunnion Mounted Ball Valves
- Floating Ball Valves
- Welded Ball Valves
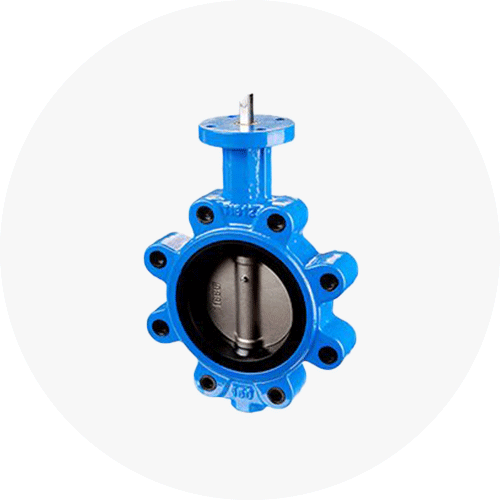
#2. Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves are quarter-turn valves that are used to start, stop, and regulate the flow of medium through a pipeline. The valve features a large disk with a stem running through it. The stem divides the disk into two pieces that look like the wings of a butterfly. A 90-degree rotation of the butterfly valve handle is used to open or close the valve.
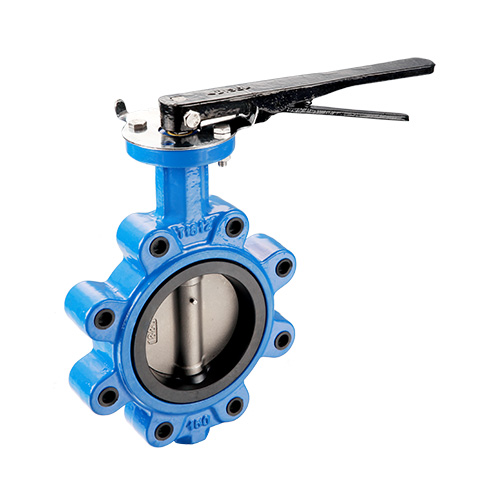

Butterfly valves are used both for shut-off applications and medium flow regulation. They are used in larger pipelines and can cope with low-pressure drop and high-pressure recovery. These valves are normally used to isolate or regulate liquid mediums used in waterworks, process industries, and power generation.
Common Butterfly Valves Used in Oil and Gas Industry
- Centric Butterfly Valves
- High-Performance Butterfly Valves
- Triple-Offset Butterfly Valves
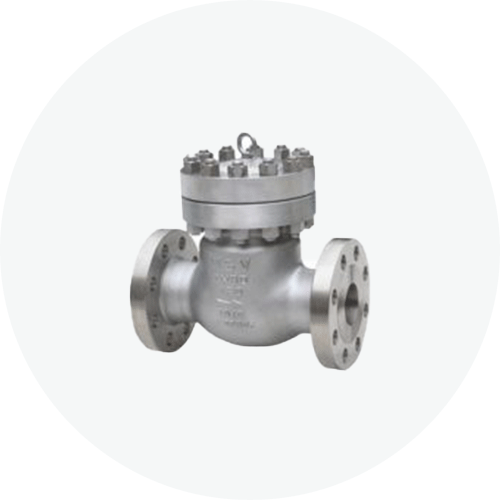
#3. Check Valves
Check valves allow the medium to flow in only one direction and prevent backflow. These valves are used to protect the integrity of machines and to make sure different mediums do not mix with each other. They are also called non-return valves or NRVs. The pressure of the flow passing through the pipeline opens the valve. Once the medium has passed through the valve, any backflow is prevented as the pressure generated by the backflow closes the valve.
Check valves are usually installed around pumps and compressors where backflow can damage the machinery or cause an unnecessary shutdown of the equipment. They are normally used fully open or fully closed and for the regulation of steam, gas, and other fluid services.
Common Check Valves Used in Oil and Gas Industry
- Swing Check Valves
- Piston Check Valves
- Ball Check Valves
- Tilting Disc Check Valves
#4. Globe Valves
Globe valves are linear motion valves that are used to start, stop, and regulate the flow of medium through pipelines. These valves can be used for isolation and throttling services. Globe valves feature a disk that is either completely removed from the flow path or it completely closes the flow path. This is the reason why they provide better shut-off than gate valves.
Globe valves are used in fuel oil systems where the flow is regulated and leak prevention is important. They are also used in cooling water system, turbine lube oil systems, air extraction condenser, and condenser air systems.
Common Globe Valves Used in Oil and Gas Industry
- Stop Check Valves (SDNR)
- Tee Pattern Globe Valve
- Wye Pattern Globe Valve
- Angle Pattern Globe Valve
#5. Gate Valves
Gate valves are bi-directional valves that are used to start or stop the flow of medium through a pipeline. These valves feature a gate that moves up and down to open and close the valve. Gate valves can be either fully open or fully closed. They are used to start and stop the flow but cannot be used for regulating or throttling applications.
Gate valves are commonly used to regulate the flow of water, oil, gas, steam, and other fluid services. They provide low-pressure drops and can work with high-pressure and high-temperature applications. The only con to using gate valves is that they are prone to corrosion and cannot be quickly opened and closed.
Common Gate Valves Used in Oil and Gas Industry
- Wedge Gate Valves
- Knife Gate Valves
- Parallel Slide Gate Valves
- Pipeline Slab Gate Valves
#6. Plug Valves

Plug valves feature disks that are conical or cylindrical and tapered that rotate to start or stop the flow of medium through a pipeline. The horizontal disk usually has a hollow side. When the hollow side is parallel to the flow, the medium can pass through unobstructed. As the disk rotates, the hollow side follows suit and the flow of medium is blocked.
Plug valves usually have more than one port, so they can be used to separate the flow of different kinds of mediums. However, the tapered disk of a plug valve means they have reduced port. This means they require more force to actuate. They are smaller in the size and have minimum resistance flow.
Common Plug Valves Used in Oil and Gas Industry
- Lubricated Plug Valve
- Non-Lubricated Plug Valve
- Centric Plug Valve
- Expanding Plug Valve
What are the Applications of Valves in Oil and Gas Industry?
Oil and gas exploration and operations have become more complex over the ages. As explorers need to dig deeper to extract crude oil and natural gas, they have to face extremely high-temperatures (greater than 1,500 For 816 C) and high pressures (greater than 25,000 PSIG) and extremely low temperatures like cryogenic (-150 F or -101 C) or cryogenic for LNG (-260 F or -162 C). Hence, the valves needed for these piping systems have to be durable, strong, resilient, and most of all reliable. For example, deep-sea valves operating 10,000 feet below the sea surface should be able to handle the low temperatures and high-pressure flow of materials, while those exposed to the extreme temperatures found in a desert need to protect both the machinery and the medium flowing inside from any contamination.
For upstream operations in the oil and gas industry, valves need to control the flow of crude oil and natural gas from high-pressure injection systems to choke valves as well as blow-out preventers at the top of wells. Since exploration and production operations usually have to work in extreme conditions, the valves used in this stage need to be strong, durable, non-corrosive, and fully leak-proof. They also have to be suitable for high-temperature, high-pressure applications. Gate valves made of higher alloy materials and ball valves are most suitable for upstream operations.

Midstream applications require the transportation of oil and gas. There are two kinds of pipelines used in the energy industry, ones that transport crude oil and others that transport natural gas. Within each pipeline system, there are smaller pipelines that are required for specific applications. For example, oil pipelines transport crude oil collected from the source to a refinery. Once refined, another set of pipelines transport refined the oil to the end-users. No matter what kind of pipeline is used, it needs to have highly reliable isolation valves that guarantee proper function and protection. Normally full-port gate and ball valves made of different kinds of materials are used in midstream applications. Compressor stations usually use nozzle check valves with low pressures and rapid responses to changes in the flow to energize the media for long pipelines.
Downstream operations like refining are marred with harsh environments. High-temperature environments can cause a phenomenon called delayed coking that can add extreme pressure on the valves damaging them. Coking fines are also highly abrasive so they can easily damage the seat, disc, stem, and other components of a valve. Downstream applications usually employ high-quality, sturdy gate valves that heat-dissipating fins and remotely controlled operating systems.
How to Choose the Right Natural Gas Shut-off Valve Types?
Choosing a suitable shut-off valve type for petrochemical applications is not an easy task. Since these devices are available in various types, it is vital to understand the application before investing in a particular one. Some of the most common valves used in the oil and gas industry for piping applications include:
- GLOBE VALVE
A globe valve is an isolating device used for shut-off applications within the industry. It is perfect for regulating the media, liquid or gas, and many other steam and condensate purposes. Although its actuation is usually manual, it may also be electric, hydraulic, and pneumatic. This valve is ideal for higher pressure and high volume systems but is less suitable for viscous and contaminated fluids.
- PISTON VALVE
A piston valve is used either fully open or closed for on/off regulation on steam and gas but typically on fluids that cause excessive seat wear. This device is usually used where the valve body needs to be permanently installed, with minimal maintenance.
- GATE VALVE
In the petrochemical industry, a gate valve is used in a fully open or closed position to regulate the flow of fluids through the pipelines. Such fluid services may include gas, steam, water, and oil. It is vital to note that a gate valve is not recommended for throttling applications.
- BUTTERFLY VALVE
A butterfly valve is ideal for use in the oil and gas industry because of its shut-off applications in larger pipelines, especially in waterworks, process industries, HPI, and power generation. It has a relatively simple build, an eccentric design for steam systems, and is ideal for liquid systems. One may control it using a handwheel, air motor, electric motor, hydraulic actuator, or pneumatic actuator.
- BALL VALVE
A ball valve can handle several types of fluids in the petrochemical industry but has a limited maximum pressure rating. It is suitable for a wide range of steam and condensate applications.
All these valves are employed in the petrochemical industry to start or stop the fluid flow through the gas pipelines, modulate, control, change, and regulate the fluid flow, protect the piping system from over or back pressure, and filter the debris to protect the equipment from damage. The valves having forged steel bodies are used in the oil and gas industry to offer high resistance to pressure and temperature. They are further classified according to their disc type, actuation type, size, and design.
Conclusion
All valves can start and stop the flow of medium through any piping system. However, not all valves are the same. For example, gate valves are more suited for high-temperature, high-pressure on/off applications where the valve is used infrequently. But they can only carry liquids and viscous liquids, Ball valves can be used to regulate the flow of slurry or corrosive materials as well. No matter what valve you require, SIO houses a wide variety of high-quality valves that can be used for a number of applications across different industries. What’s more, it offers valve customization service and manufacture for specific valves.
Our extensive network of sales and lifelong consulting services means you will get a quality product at incomparable prices. We distribute our products to North and South America, Middle East, South East Asia, Africa, and beyond. Get in touch with one of our esteemed engineers today.