Table of Contents
Valves are an integral part of any industrial unit or system. Industrial valves are used to regulate the flow of the medium through pipelines, isolate certain areas of the pipeline, check the system integrity of a unit, and more. This is the reason why industrial valves need to be of the highest quality, leak-proof, efficient, and durable.
The debate of which is better between cast steel and forged valves has been going on for ages. For the longest time, cast steel valves dominated the industrial space. They were a cost-efficient, quick-to-manufacture, high-quality valves that performed well in different industries. But then forged valves hit the market and the landscape was changed. Forged steel valves promised more strength, longevity, and better performance. They were also great for high-temperature, high-pressure applications. Hence the debate of which is better began and is still ongoing today.
In this blog, we will go through the definitions of cast and forged steel valves, how they are made, what makes them different, and which one is better for what application. Read on to find out more.
What are Cast Steel Valves?
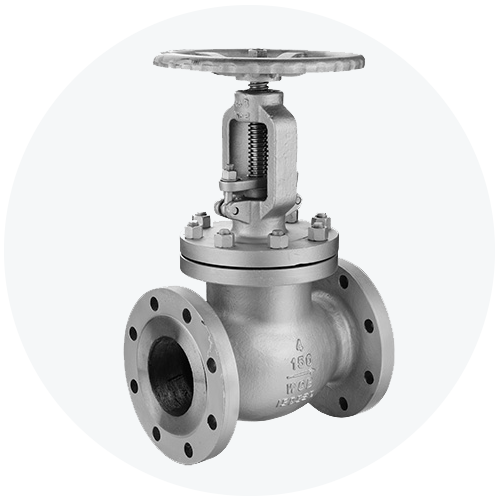
Cast steel valves are manufactured using a process called ‘casting’. This method requires the steel to be melted and then molded into the desired shape. Modern cast steel valves are very competitive in terms of strength, longevity, quality, and wear resistance. For example, SIO Cast Steel Valves are used extensively in petrochemical plants, power generation plants, waste processing units, water treatment plants, railways, and more.
Cast steel valves can be made from high-grade steel or metal alloys depending upon the nature of the application. Since they are made through molds, you can customize these valves easily to have complex shapes or intricate details. They can be made in any size and a single valve can have many different components.
Types of Casting
Casting is a process whereby metal is melted and then the molten liquid is poured into different molds. However, there are different ways of casting metal like sand casting, pressure casting, investment casting, cavityless casting, gravity casting, shell mold casting, low-pressure casting, and more. Here we are going to discuss two of the most common types of casting used to make cast steel valves.
Sand Casting
Sand casting is the most common type of casting method used to make cast steel valves. In this method, the molded pattern for the valve is fitted to the bottom of the sandboxes. These boxes are then filled with casting sand. The sand is then pressed firmly into the molds. Then the sandboxes are turned upside down and the molded patterns are removed. But since the sand was pressed around these molds, the impression of the mold is imbedded in the casting sand. Check the video of sand casting here.
Two parts of the sandbox are then fitted on top of each other and bolted together. Melted steel is poured on top of the bolted sandboxes that seeps through holes in the top of the box. The bolted sandbox is then cooled. Once the sandbox is unbolted and removed, the steel cast valve component is revealed. Cut off any access steel around the component and it is ready to be used. Sand casting is used to create larger valve components as this tends to be a more expensive form of casting.
Investment Casting
Investment casting is a process that is used to manufacture smaller, more precise components of cast steel valves. In this process, the first mold is made using hard wax, lost wax, lost foam, or similar material. This wax mold is then dipped in wet ceramic slurry until it becomes really thick. Once dried, the wax is melted so that the ceramic mold is left behind. Check the video of investment casting here.
The ceramic mold is heated to a temperature of about 1000 degrees and molten metal is poured into the hot ceramic mold. Once the metal cools, the ceramic mold is broken using vibrations leaving behind precise metal components. Investment casting is used to create smaller parts up to 100 kg and 1.5m of maximum length. This method is also more cost-effective than sand casting but cannot be used to create larger components.
What are Forged Steel Valves?
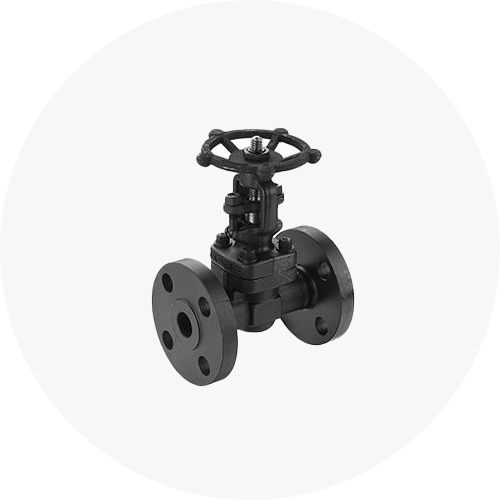
Forged steel valves are manufactured using a process called ‘forging’. Forging is based on the application of thermal energy to solid blocks of steel and then using mechanical forces to further process the steel into a finished product. This process is used to make valves that are extremely strong and tough. For example, SIO Forged Steel Valves like forged steel gate valve are used in mining and mining processing, agriculture and livestock handling, aeronautics, automobile industry, brickworks, stormwater plants, rendering plants, asphalt plants, power and water industry, pharmaceuticals, chemical industry, cosmetic industry, and more.
Forged steel valves are perfect for handling high-temperature, high-pressure services. However, you can only some metals can be used in forging. This method is used to make smaller, specialized valves. Larger forged steel valves have to be made in components. The components are then welded or connected through flanged connections to make the complete valve.
Types of Forging
The process of forging is completed in a number of steps. First, the raw material that is in the form of blocks, ingots, or billets is cut into smaller pieces. The pieces are then heated to reach the required temperature at which the metal will be ductile and malleable. Once the metal is heated, it is then transformed into the required shape by applying mechanical forces. In olden times the pressure was applied manually through power hammering. Now automatic machines like hydraulic presses are used to get the job done.
Source: https://www.powerengineeringint.com
Once the metal is shaped into the desired form, it undergoes machining, finishing, and heat treatment to get the finished product. Forging has the following classification based on the temperature applied to the raw metal:
Cold Steel Forging
This type of forging is done at room temperature without applying any additional heat to the metal. The metal has lower malleability than in case of hot or warm forging so a greater mechanical force is required to shape the metal.
Warm Steel Forging
In this type of forging the metal is heated to temperatures ranging from 800 to 1000 degrees centigrade. The metal becomes ductile at this temperature but no as much as in hot forging.
Hot Steel Forging
When the metal is heated to temperatures over 1000 degrees (but still below 1300 degrees), it is called hot steel forging. The metal becomes so malleable at this temperature that only a moderate amount of mechanical pressure is required to mold it into the desired shape.
There are also two types of forging depending on the method used to shape the metal components of the valve.
Closed Die Forging vs Open Die Forging
In closed die forging, the melted metal is placed in the bottom die and it is almost the exact shape and size of the final forged part. In open die forging, the melted metal is moved through multiple dies that shape part of the metal into the desired shape through hammering or stamping. Here is a diagram that shows the difference between these two types of forging.
Source: https://blog.projectmaterials.com
Cast Steel Valves vs. Forged Steel Valves
Now that we know how cast steel valves and forged steel valves are made, let us take a look at some of their merits and demerits.
Merits of Cast Steel Valves
- Flexibility in Design: Cast steel valves are made from liquid metal so they can be cast into any kind of shape or size easily. You can also achieve greater complexity of the design and make intricate working parts for the valve.
- Variety: Cast steel valves have a greater variety in terms of the metal composition. Different kinds of metal alloys can be used to make cast steel valves, like cast steel globe valve. You can choose exact specifications like enhance corrosion-resistant by using the right combination of metals.
- Reduced Machining: Cast steel valves don’t need to go through a lot of machining to be manufactured. This translates to less machining costs and quicker turnover time.
- Wide Availability: Unlike forged steel valves, cast steel valves are more widely available. This is because the process of casting is less complicated and expensive than forging. Replacement parts and valve servicing is more easily available.
- Space-Saving Design: Cast steel valves have a contoured shape with round edges. This makes them easy to install even in small spaces and pipelines.
Demerits of Cast Steel Valves
- The process of casting generates a lot of material waste. Some material is lost when the metal is melted down into a liquid. The liquid is then reworked as it is put into and removed from molds. In each step, a part of the core material is lost as waste.
- The process of solidifying cast steel valves can sometimes produce small impurities like cracks and voids in the valve. This can lead to lower mechanical properties that can only be repaired by time-intensive and costly weld repair.
- When cast steel valve components are welded together, the heat treatments can alter the microstructure of the castings. This results in higher creep and lower hardness of the valve. Rigorous inspection is required to make sure the valve has retained its strength and creep resistance after being welded
- Cast steel valves have lower testing parameters than forged steel valves which means you need to be very careful when ordering these valves. Professional industrial valve manufacturers like SIO make sure to include the right certifications and testing for each cast steel valve but that isn’t the case everywhere.
Merits of Forged Steel Valves
- Less Waste: Since forged steel valves are made from a solid block of metal, there is less material waste produced in the process. The metal is not reworked as much as it is in casting which reduces waste as well.
- Stronger and Durable Product: The immense pressure applied on the heated metal ensures there are no internal cavities or voids in the finished product. Surface porosity is also reduced. All of this leads to a finished product that retains its structural integrity and has higher ductility and tensile strength.
- Reduced Thermal Fatigue: Forging produces steel valves that have less wall thickness which means the valve has a smaller temperature gradient. The valve requires less time to reach equilibrium and is thus less prone to thermal fatigue. Power plants that cycle through start-up and phase-down on a daily basis can really rely on forged steel valves.
- Better Mechanical Properties: Forging creates mechanically strong parts without the need for expensive alloys. The steel grain structure of the metal gets modified to retain the shape of the final product with highly uniform composition and metallurgical recrystallization.
- High-Resistance Valve: Steel valves created through forging can easily handle high loads and stress and have high wear resistance. They are able to stand stronger impacts and can manage high-temperature and high-pressure applications without the need for any modifications.
Demerits of Forged Steel Valves
- The process of forging is cost and energy-intensive. The process of machining and refining the end product takes a lot of time and energy. This is the reason why forged valves have a longer turnover time.
- Forged steel valves cannot be made in all kinds of shapes and sizes. In fact, they are preferred to make smaller valves and valve components as larger valves can only be made in parts and get very expensive.
- Larger valves are developed in parts that are then welded or connected through flanged connections. In either case, there is an added risk of leakages where the individual parts are connected to each other.
Conclusion
Choosing the right valve for your application depends on a number of factors. While forged valves are great at handling high-temperature, high-pressure applications, they are expensive and cannot be easily standardized. Cast valves and carbon steel valves are cost-effective and can be produced in greater numbers easily. However, there is always a risk of a void in the valve’s construction. To find out which kind of valve is the best you need an experienced valve manufacturer that can advise you on the most appropriate steel valve which meets specific plant needs. Get in touch with us because our valves are API 602 certified. If you want to look for the best industrial valve in China, check this best valve manufacturers guide in China.